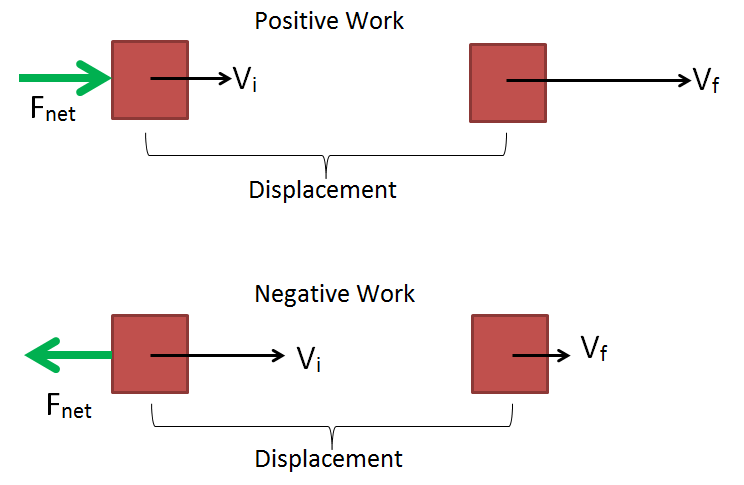
how are work and energy related explain the work-energy theorem
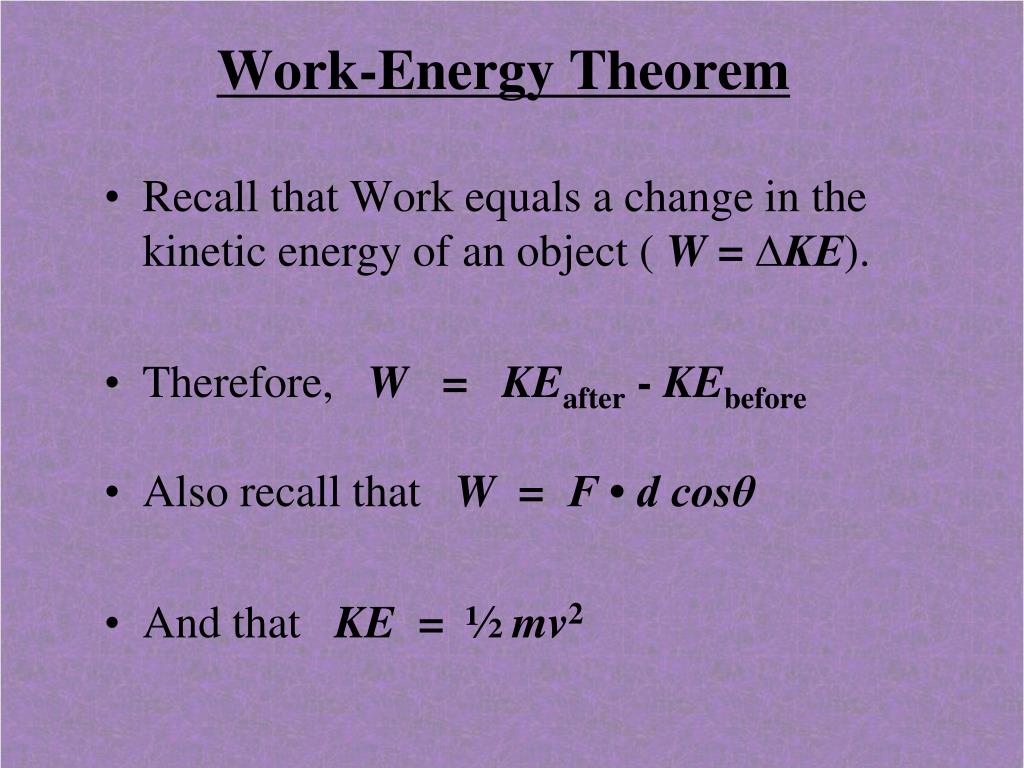
The quantity 1 2mv2 in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass m moving at a speed v. For example consider the following figure According to Work energy theorem Work done by all the forces Change in Kinetic Energy.
Work Energy Theorem Work Energy Power 2 In Hindi Youtube
Suppose if a force is applied to a body and the body does not move or the.

. Work-Energy Theorem Definition The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on a body is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the body. For example when a ball is pushed with a force F the force does the work on the ball and provides energy to the ball. Derivation of the Work-Energy Theorem It would be easy to simply state the theorem mathematically.
The work done by this force is equal to the change in momentum of the system m due to this force F. Overview of Work-Energy Theorem. Work energy theorem concluded that if no external work is done then the Kinetic energy before a process must be equal to its Kinetic energy.
The quantity 1 2mv2 1 2 m v 2 in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass m moving at a speed v. The net work on a system equals the change in the quantity 1 2mv2 1 2 m v 2. K E 1 2 m v 2.
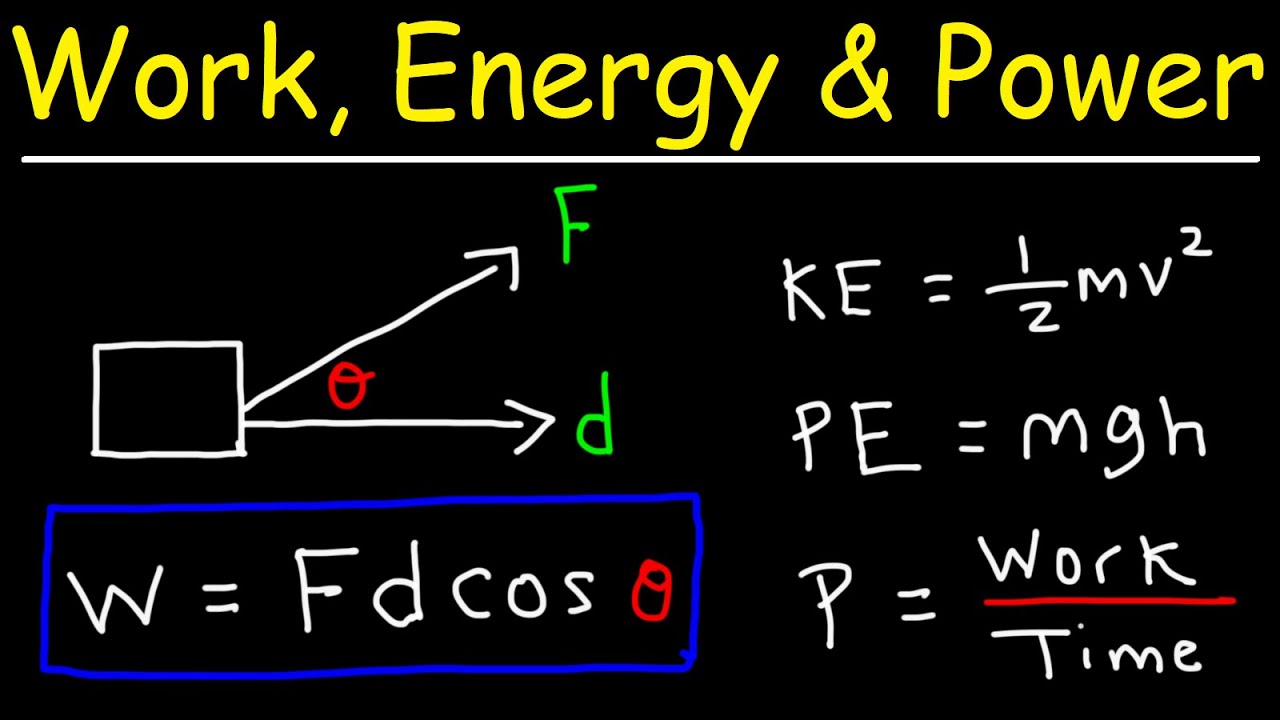
Concepts of Potential Energy. Work is defined as the product of force F and displacement S in the forces direction. Browse more Topics under Work Energy And Power.
In contrast energy is the capacity to do work. W g W N W f K f K i. When the regular speed of the particle is constant then there is no change in Kinetic energy and the work done by the resultant force is zero.
Lifting weight from the ground and then putting it on the shelf is an excellent example of work done. Work done force multiplied by displacement. By the way many individuals use W pressure x distance however correctly work is the web pressure on a system built.
This expression is called the work-energy theorem and it actually applies in general even for forces that vary in direction and magnitude although we have derived it for the special case of a constant force parallel to the displacement. Just as force was related to acceleration through F ma so is work related to velocity through the Work-Energy Theorem. Answer 1 of 4.
For a slightly longer explanation of this work is defined as the force times the displacement if. The force equals the objects weight and the distance equals the height of the shelf. However an examination of how the theorem was.
The translational kinetic energy of a body is equal to one-half the product of its mass m and the square of its velocity v or 12mv 2. Work is the application of force over a given distance on an object. After the net force is removed no more work is being done the objects total energy is altered as a result of the work that was done.
Work done KE f-KE i Network done change in Kinetic Energy. Consider a force F applied to a mass m. In our everyday language work is related to expenditure of muscular effort but this is not the case in the language of.
The concept of work in physics is much more narrowly defined than the common use of the word. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. The work we do on the rock also equals the rocks gain in gravitational potential energy PEe.
Where K f Final kinetic energy. The subscripts 2 and 1 indicate the final and initial velocity respectively. 10 N 10 kgms 2 so 10 J 10 kgm 2 s 2.
The work done on the cart is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the cart. The work done on the system can thus be represented as a function of the final velocity squared. W F x d.
The work-energy theorem explains the idea that the net work - the total work done by all the forces combined - done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object. W P E e m g d. Mathematically E W.
Features of the work-energy theorem is. The Work-Energy Theorem states that work is equal to the change in kinetic energy as mentioned below but thats not the whole story. The theorem implies that the net work on a system equals the change in the quantity latexfrac12mv2latex This quantity is our first.
Since the cart starts from rest the initial kinetic energy of the cart is 0 J. W N work done by a normal force. This is a statement of the workenergy theorem which is expressed mathematically as.
The work-energy principle or work-energy theorem relates the work done by all forces acting on an object to its energy. W Δ K E 1 2 m v 2 2 1 2 m v 1 2. Kinetic energy depends on the mass of an object and its velocity v.
A State and explain the work-energy theorem of a particle. In this lab we will test the work energy theorem using. 3 b Explain with examples conservative and non-conservative forces.
Where W g work done by gravity. When we drop the rock the force of gravity causes the rock to fall giving the rock kinetic energy. This theorem was proposed and successfully tested by James Joule shown in Figure 92.
When a body is subjected to a force it causes the body to move and one can say that some work is done by the force. Work is done on an object when an applied force moves it through a distance. W net 1 2mv2 1 2mv2 0 W net 1 2 m v 2 1 2 m v 0 2.
It states that the total amount of work done on an object is equal to the. The place W is the work and E is the change of vitality because of the work. W Δ K E 1 2 m v 2 2 1 2 m v 1 2.
4 c A neutron is found to pass two points 6 meters apart in a time interval of 18 104sec. Now that we have a definition of work we can apply the concept to kinematics. The work-energy theorem states that the work you set right into a system is transformed into the vitality of the system.
Also here the work done is the work done by all forces acting on the body like gravity friction external force etc. The work-energy theorem states that the net total work done on a system is equal to its increase in kinetic energy. W net Δ E k E k f E k i The work-energy theorem is another example of the conservation of energy which you saw in Grade 10.
To learn how the Work-Energy Theorem is derived we must first learn the nature of work as a scalar quantity and how two or more vector quantities are multiplied. The theorem states that the work done by all the forces acting on a particle is equal to the particles kinetic energy. Here W is the work done in joules J and ΔK is the change in kinetic energy of the object.

A State And Prove Work Energy Theorem In The Case Of Const Scholr

Homework And Exercises Can The Work Energy Theorem Be Applied In This Case Physics Stack Exchange

Homework And Exercises Can The Work Energy Theorem Be Applied In This Case Physics Stack Exchange
Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Work Energy Theorem And It S Physics Brahmatrix Facebook

Work Energy Theorem Geeksforgeeks

Work Energy Theorem Review Article Khan Academy

Work Energy Theorem Classical Mechanics By Farhan Tanvir Tushar Open Physics Class Medium

Example Using The Work Kinetic Energy Theorem Youtube

Energy Work Power 18 Of 31 Work Energy Theorem Calculate The Velocity Of An Object Youtube
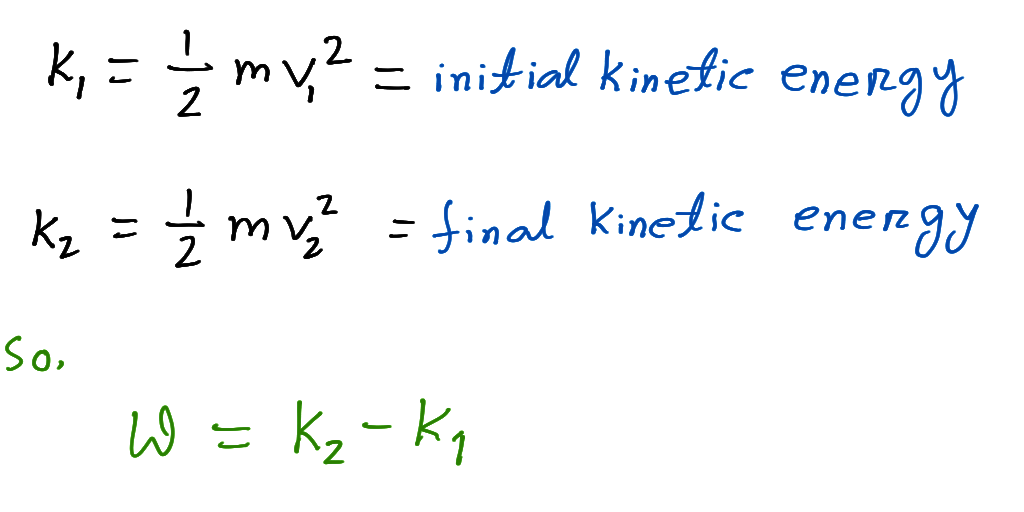
Work Energy Theorem Classical Mechanics By Farhan Tanvir Tushar Open Physics Class Medium
Ppt Work Energy Theorem Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5571805

Kinetic Energy And The Work Energy Theorem Physics

The Work Energy Theorem Objectives Investigate Quantities Using The Work Energy Theorem In Various Situations Calculate Quantities Using The Work Energy Ppt Download

Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube